In modern manufacturing, the casting process is one of the most common manufacturing methods, which produces parts of various shapes and sizes by injecting molten metal into a mold and leaving it to cool and solidify. Different types of metal casting methods are suitable for different materials, accuracy requirements and production scales. This article will introduce several common casting process, and discuss their advantages and disadvantages, application areas and how to choose the most suitable casting process.
The basic principle of casting process
The basic principle of the casting process is to heat the metal or other materials to a molten state, and then injected into a pre-prepared mold, cooling and solidification to form a predetermined shape of the part.
The process usually involves several major steps:
Mold making: making a mold, which can be made of different materials such as sand, metal, etc.
Melting: Heating the metal to its melting point to make it liquid.
Pouring: The molten metal is poured into the mold.
Cooling and demolding: The metal is cooled in the mold and the molded casting is eventually removed.
Post-treatment: The casting may require removal of excess metal, trimming, polishing or heat treatment to improve its performance and appearance.
The following will introduce the five common casting processes and their advantages and disadvantages and applicable occasions:
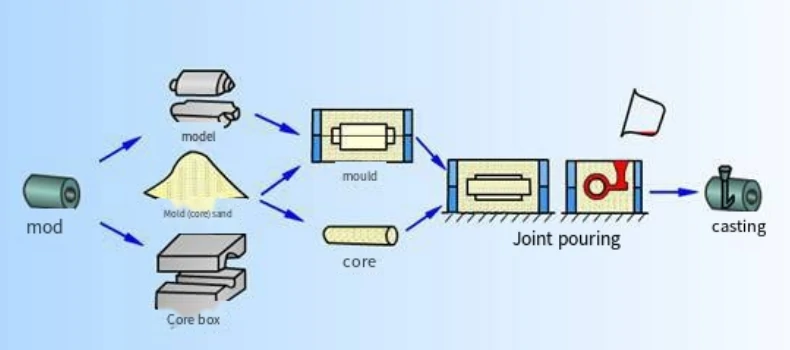
1.Sand casting
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most widely used casting methods. It is made by mixing sand and clay to make molds for casting a variety of metals and large size parts.
Advantages:
Low cost: the cost of making molds is relatively low and suitable for small batch production.
Wide range of applicable materials: can use a variety of metals, such as iron, aluminum, copper, etc..
Large degree of freedom of design: able to cast complex shaped parts.
Disadvantages:
Lower precision: sand casting castings have rough surfaces and usually require subsequent processing.
More defects: common casting defects include air holes, sand holes, cracks, etc.
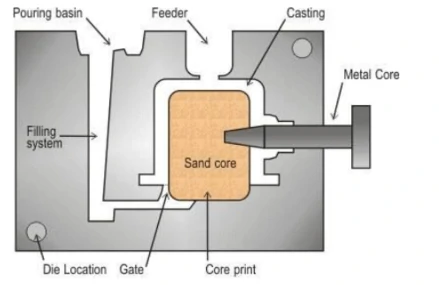
2. Metal casting
Metal casting uses metal molds for casting and is suitable for medium scale production. It is commonly used for parts requiring high precision and good surface quality.
Advantages:
Short production cycle: metal molds can be used many times, reducing the time for mold making.
High precision: castings have high dimensional accuracy and good surface quality.
Suitable for mass production: the repeated use of molds is very suitable for medium mass production.
Disadvantages:
High cost of molds: the cost of making metal molds is high, suitable for mass production.
Limited scope of application: not applicable to all metals, especially high melting point metals.
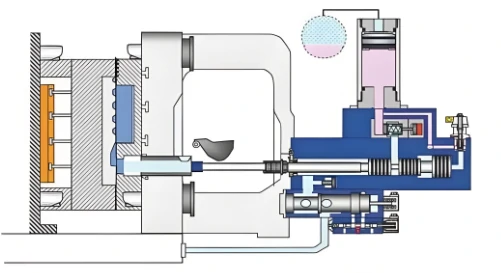
3.Pressure casting
Pressure casting is a casting method in which molten metal is injected into a mold at high pressure, and is suitable for producing precise and complex castings.
Advantages:
High production efficiency: suitable for mass production and short production cycle.
High precision and quality: castings have high dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces, reducing the need for subsequent machining.
Suitable for aluminum alloys and other materials: especially suitable for casting aluminum alloys, zinc alloys and other metals.
Disadvantages:
High cost of equipment and molds: pressure casting requires more expensive equipment and molds, with a larger initial investment.
Suitable for mass production: for small batch production, the cost of pressure casting is high.
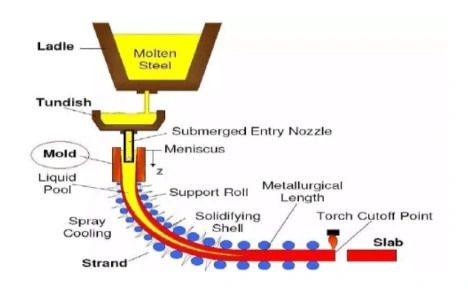
4. Continuous casting
Continuous casting is a casting method for large-scale continuous production, mainly used in the production of long castings such as metal bars and pipes.
Advantages:
Suitable for large-scale continuous production: can realize efficient, continuous casting process, high production efficiency.
Save material and energy: continuous production method can reduce waste, save raw materials and energy.
Uniform product quality: the quality and performance of castings are more stable, suitable for long time operation.
Disadvantages:
High cost of equipment: continuous casting equipment investment is large and requires long-term maintenance.
Higher energy consumption: the continuous casting process consumes more energy, especially when dealing with high-temperature metals.
![]()
5.Silicone Sol Casting
Advantages:
High precision: capable of casting complex parts with micron-level accuracy, suitable for applications requiring very high precision.
Good surface quality: smooth casting surface, reducing the need for secondary processing, suitable for parts requiring fine surface treatment.
Suitable for high-temperature alloys: capable of casting high melting point metals and alloys, especially suitable for casting high-temperature and corrosion-resistant alloys, such as nickel-based alloys.
High material utilization: high precision casting reduces scrap and improves material utilization.
Repeatability: suitable for small batch, high-precision production, can maintain high consistency.
Disadvantages:
Higher cost: due to the need for special coatings, molds and high-precision equipment, silicone sol casting is more expensive.
Complicated process: the steps of coating, drying and dewaxing are tedious, and each step needs to be strictly controlled.
High equipment requirements: High-precision molds and special equipment are required, with large investment in equipment and high maintenance difficulty.
Difficulty in operation: the process has high technical requirements for operators, and improper operation may lead to casting defects.
Limited scope of application: mainly applicable to small batch, high-precision casting, not suitable for large-scale low-precision production.
Areas of application for casting processes
Different casting processes are used in different industries and products.
The following are examples of applications in several major fields:
Automotive industry: engine components, transmission systems, brake parts, etc. Sand casting, pressure casting and metal casting are often used.
Aerospace: parts requiring high precision and strength, such as turbine blades and engine components, are often precision cast.
Construction and infrastructure: steel structures, pipelines, etc., usually using continuous casting and sand casting.
Machinery and equipment: such as pump bodies, gear boxes and other heavy machinery parts, often using metal mold casting and pressure casting.
Arts and decorations: sculptures, monuments, ornaments, etc., usually using precision casting.
How to choose the right casting process
When choosing a casting process, you need to consider the following factors:
Product shape and complexity: If complex geometries or high-precision parts are required, investment casting or pressure casting may be the best choice.
Production quantities: for small production quantities, sand casting or pouring is more economical; while for large production quantities, pressure casting and continuous casting can provide higher efficiency.
Type of material: Different casting processes are suitable for different types of metal materials, and the choice needs to be based on the metal being used.
Cost considerations: if the budget is limited, you can choose a lower-cost casting methods, such as sand casting; and for the need for high precision and high quality castings, may require a higher cost of precision casting.
Conclusion
Through the understanding of different types of metal casting processes, we can see that each casting methods has its unique advantages and disadvantages and scope of application. According to the product design requirements, production scale, material properties and cost budget, a reasonable choice of suitable casting process is essential to optimize the production process and improve product quality. We hope that through this article, you can have a more in-depth understanding of the casting process, and can make the most suitable choice.







